

Experiencing a code blue alert in a hospital setting for the first time is one of the most unforgettable experiences of nurses in their career. It can be scary for new nurses as it always happens unexpectedly. Every minute is important as the chance of revival decreases with time. There are trainings provided for nurses so they will be skilled in responding to code blue situations appropriately.

Code blue is the term used by most medical institutions to indicate that a patient is having cardiopulmonary arrest and needs immediate resuscitation. The resuscitation is done by the “code team” of the hospital but initial resuscitation efforts should be done by the nearest nurses on duty. Once the code team arrives on the scene, they will continue the resuscitation efforts being done to the patient by the first responders.

The role of first responders is critical as they will start the resuscitation efforts to the patient undergoing cardiopulmonary arrest.
Here are the detailed tasks of the first responders to the code based on the guidelines of the American Heart Association:
• First Responder
– Call for help.
– Ensure patient is flat on bed. Remove pillows and drop the head of bed.
– Check for pulse. The best site for this is the carotid pulse.
– Start compression.
• Second Responder
– Bring the e-cart and other emergency equipment on the site of code.
– Secure the backboard under the patient.
– Manage airway by using an ambu bag or a pocket mask with one-way valve.
– Switch role with the first responder in giving chest compressions to the patient.
• Third Responder
– Turn on the AED/defibrillator and use it for pulseless patients.
• Fourth Responder
– Ensure that IV fluids and emergency medications are ready for use of the Code Team.
• Fifth Responder
– In-charge with documentation.

Hospitals have different code team members but it is usually composed of the following:
o Physician
– Serves as the code team leader
– Directs medical management to be followed by the rest of the Code Team
o Unit RN
– Assists the Code Team as needed
– Initiates basic life support.
o Critical Care/ICU RN
– Serves as the code team leader until the physician arrives
– Manages and monitors defibrillator and cardiac rhythm strips
– Relays ECG findings to the physician and to the nurse documenting the code
– Administers emergency drugs as directed
o Pharmacist
– Prepares emergency medications
– Calculates infusion rates
– Ensures drug incompatibilities are avoided
– Ensures the e-cart is properly restocked
o Respiratory Therapist
– In-charge of airway management and respiratory assessment
– Assists in intubation
– Secures settings of mechanical ventilator
– Obtains and reports arterial blood gases as ordered
o Clinical Supervisor
– Facilitates communication between the physician and the patient’s family
– Assists patient’s family in the waiting area as the code progresses
– Facilitates transfer of patient to a critical care unit once revived
– Assists nurse in charge of documentation to ensure proper recording of the events that took place
o ED Techs
– Performs chest compressions
– May serve as runner of the team
– Assists in the transfer of patient to the critical care unit once revived
Aside from the medical team, the following personnel are also important:
Security
– Assists with crowd control
– Ensures patient’s belongings are secured during the code
– Facilitates post-mortem transfer of patient’s body to the morgue if the patient will expire
Pastoral Services
– Provides emotional and spiritual support to the patient’s family
– Facilitates communication with the patient’s spiritual or religious affiliates
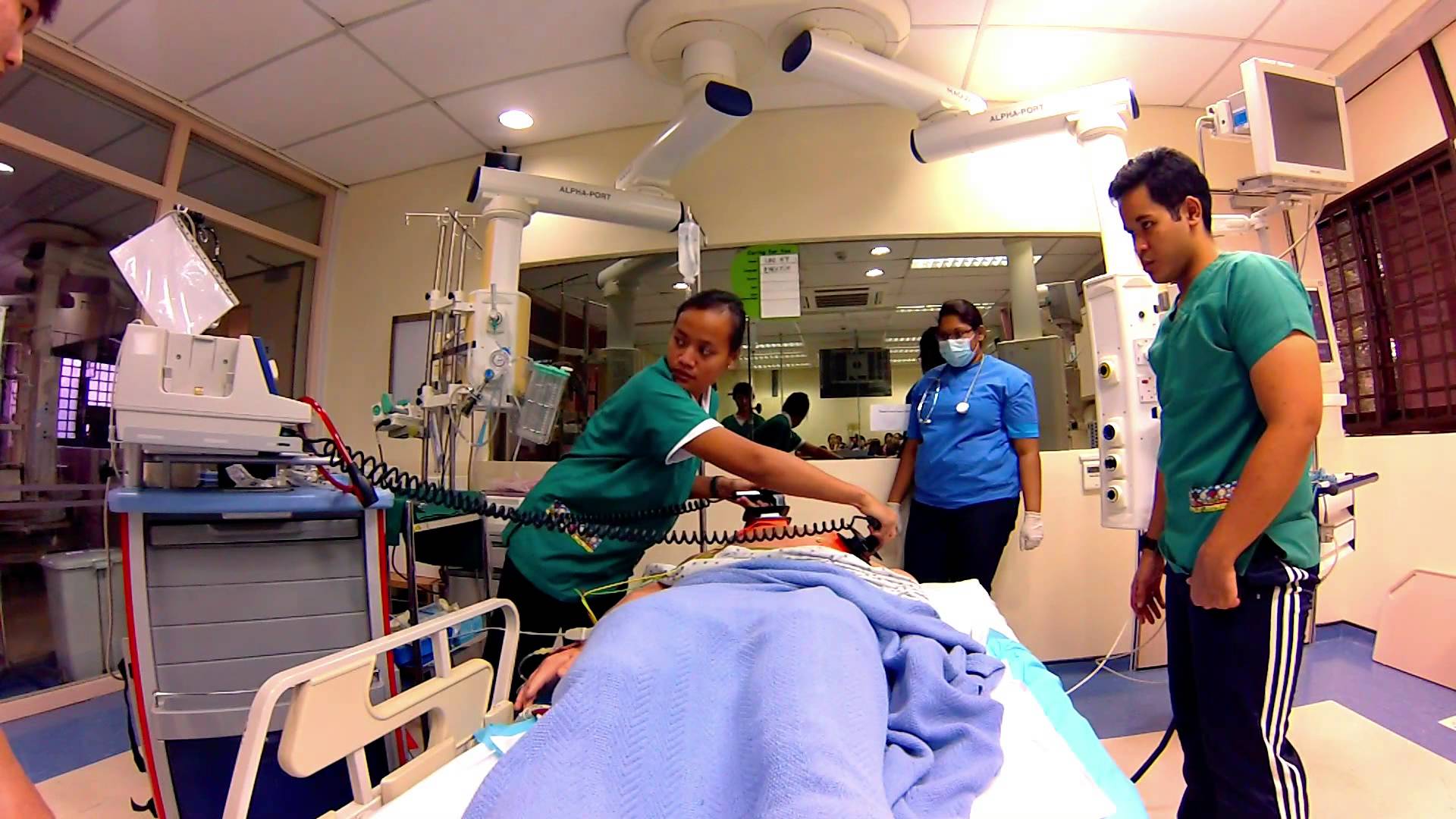
1. Get involved – Be active with the code team even if it’s your first time to be involved. It’s a rare opportunity to be involved in an ongoing Code Blue and you can gain valuable experience as a nurse.
2. Participate in mock codes – Healthcare institutions usually conduct mock codes especially for new nurses so they will be oriented with the hospital’s policies during Code Blue. You will learn all the essential do’s and don’ts by participating with these mock codes.
3. After your first Code Blue, debrief with the team afterwards – Talk with the team about the things that went well and what areas need improvement. Debriefing after the code will help you improve your skills and knowledge in responding to codes.
1. Leaving the code right away – Once the Code Team has arrived, don’t leave the scene right away. You know your patient well and the team might need some information from you as the patient’s charge nurse.
2. Switching roles without proper communication – If you feel the need to switch roles, communicate with the team to ensure someone will take place of your role.
3. Shouting – Be calm and communicate clearly. Do not shout or yell as it adds up to the tension of the team during a code. Speaking calmly also maintains your presence of mind throughout the event.
It is frightening to experience code blue for the first time as a nurse. But once you go through it, you will feel more confident in facing the tough situations in patient care. Don’t miss opportunities for learning and participate in mock codes. Get certified as well with Basic Life Support (BLS) and Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) trainings within your state.
About the Author:
Je Abarra is a Licensed Practical Nurse at Centre universitaire de santé McGill et IR-CUSM. For many years, Je wrote many amazing and informative posts for Nursebuff. She is very passionate about her profession, and loves to provide tips and fun facts about nursing and healthy living.